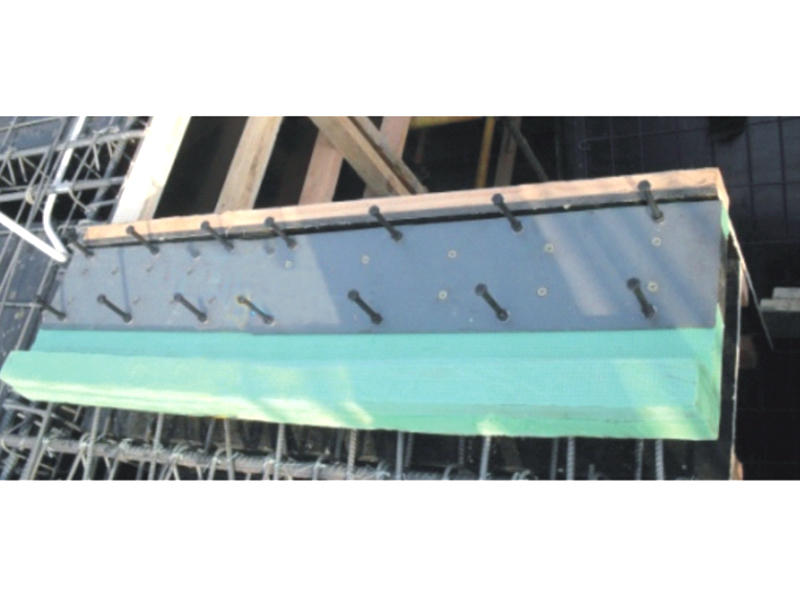
In the realm of structural engineering,
Elastic Sliding Bearings (ESBs) have emerged as pivotal components, revolutionizing the way buildings and infrastructures handle dynamic forces and adapt to environmental changes. These innovative bearings provide a flexible and resilient solution that mitigates structural stress and enhances the safety and longevity of various constructions.
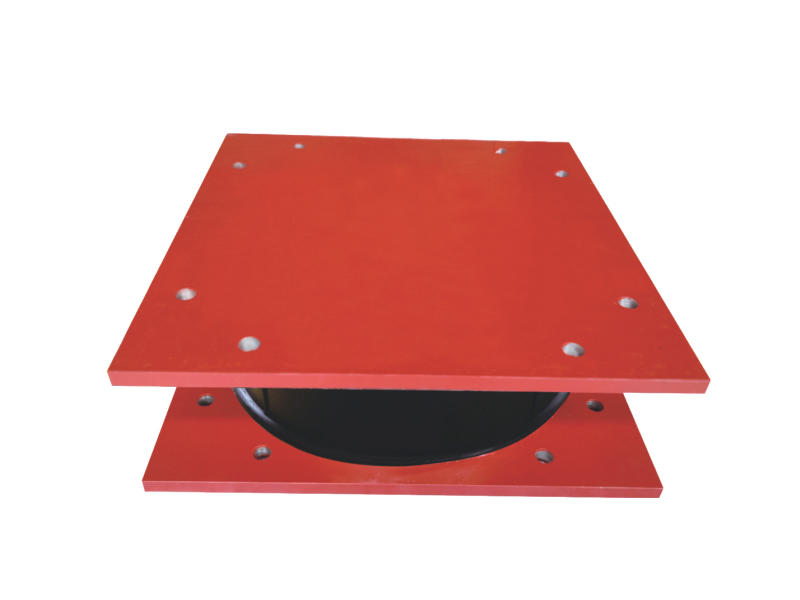
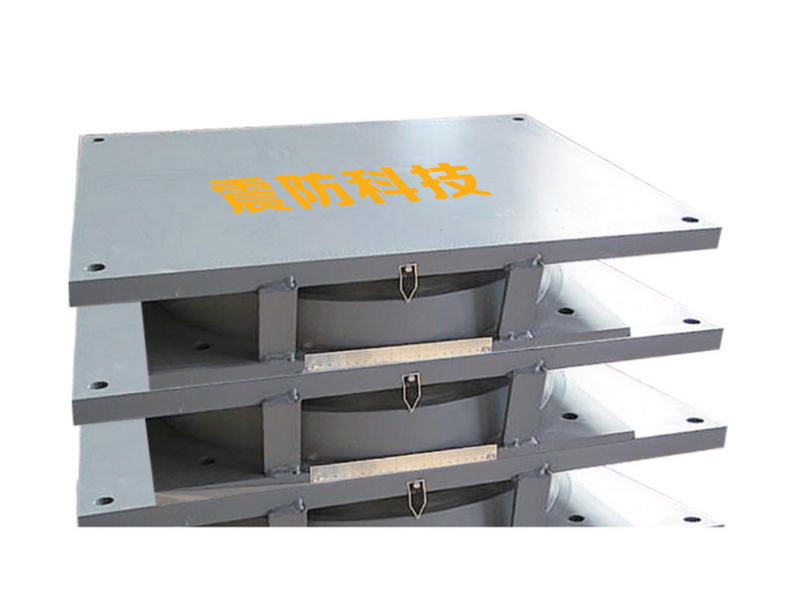
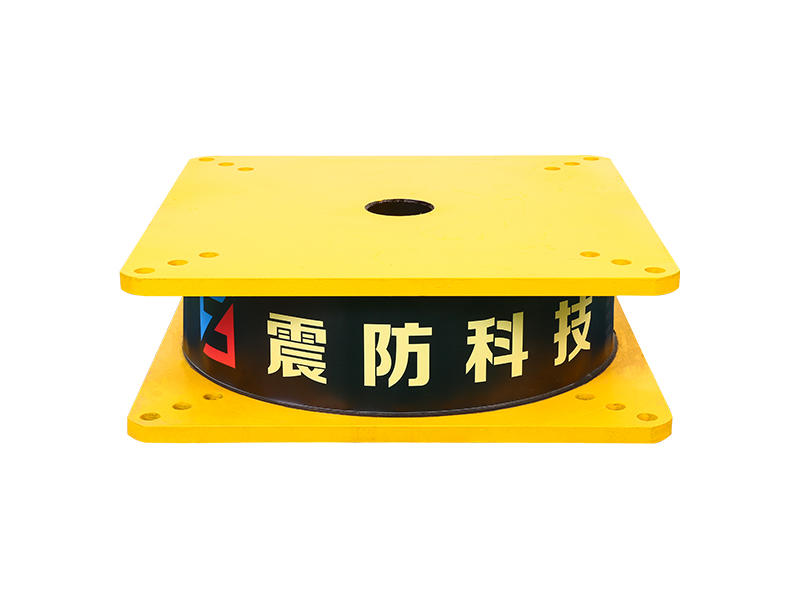
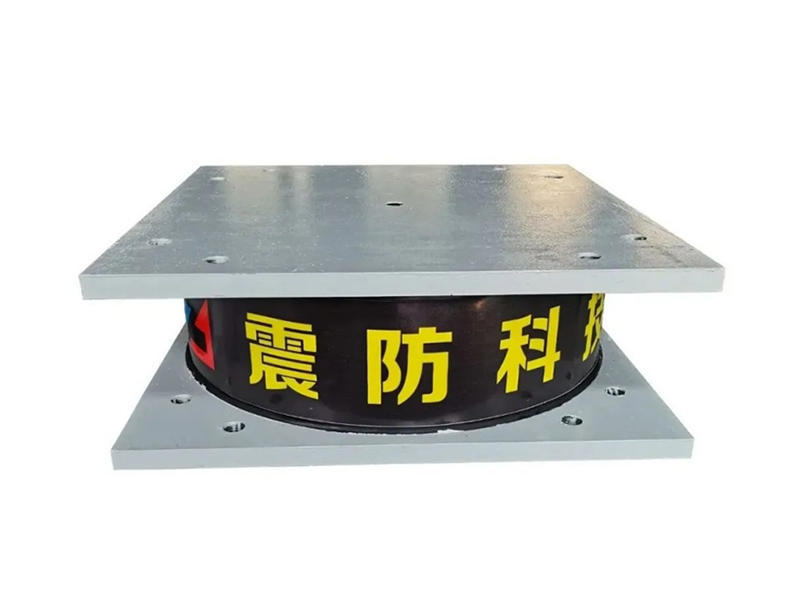
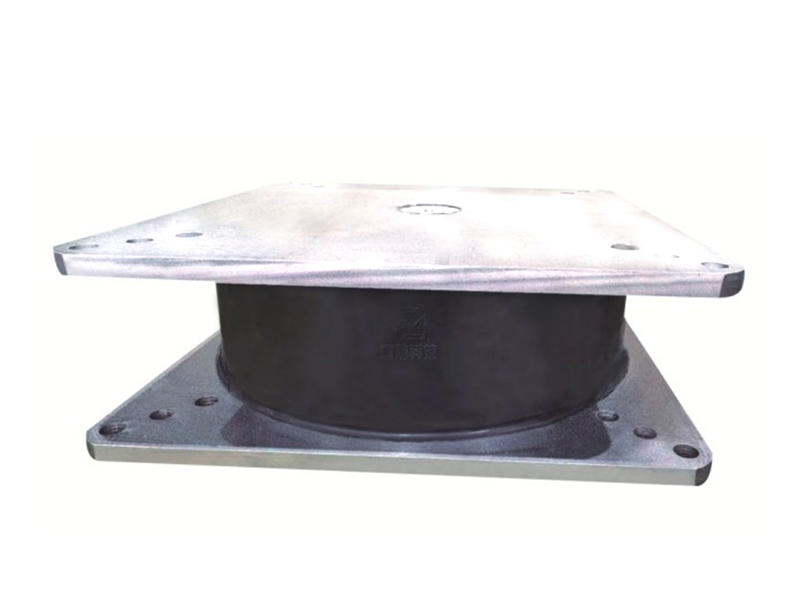
At the core of ESBs is their ability to accommodate movement and absorb vibrations within structures. Comprising layers of durable materials, such as rubber or polymers sandwiched between metal plates, these bearings offer a unique elasticity that allows controlled sliding and deformation. This characteristic enables buildings to withstand seismic activity, thermal expansion, and other forces while safeguarding against structural damage.
The versatility of ESBs lies in their application across a spectrum of infrastructure types. From bridges and high-rise buildings to industrial facilities and even historical monuments, these bearings play a crucial role in maintaining structural integrity. By facilitating controlled movement and redistributing forces, ESBs help prevent structural fatigue, cracking, or failure, ensuring the safety and durability of diverse constructions.
Furthermore, the adaptability of ESBs extends to their ability to cater to various load capacities and movement requirements. Engineers can customize these bearings to suit specific project needs, adjusting their dimensions, materials, and characteristics to accommodate anticipated forces and movement patterns. This bespoke approach ensures optimal performance and resilience tailored to each structure.
The impact of Elastic Sliding Bearings on structural engineering has been profound, particularly in regions prone to seismic activity. The ability of these bearings to dissipate seismic energy and limit structural displacement has made them indispensable in enhancing the seismic resilience of buildings and infrastructure. This resilience not only safeguards lives but also minimizes repair costs and downtime in the aftermath of seismic events.
Moreover, the use of ESBs aligns with sustainable engineering practices. Their ability to prolong the lifespan of structures by reducing wear and tear, along with the potential for reusability and recyclability, contributes to sustainable construction efforts. By enhancing the durability and safety of structures, ESBs support the principles of eco-friendly and resilient infrastructure.
In conclusion, Elastic Sliding Bearings (ESBs) represent a remarkable innovation in structural engineering, offering a dynamic and versatile solution to address the challenges posed by dynamic forces and environmental factors. Their ability to accommodate movement, absorb vibrations, and enhance structural resilience marks them as essential components in ensuring the safety, longevity, and sustainability of various constructions.
As the demand for resilient and adaptive structures continues to grow, ESBs stand at the forefront, contributing significantly to the advancement of structural engineering. Their impact in mitigating risks, enhancing safety, and promoting sustainability underscores their pivotal role in shaping the future of infrastructure across the globe.