The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEAs the frequency and intensity of seismic events around the globe continue to increase, the need for resilient infrastructure that can withstand the forces of earthquakes has become paramount. Earthquakes can cause catastrophic damage to buildings, to loss of life, financial setbacks, and long-term displacement for communities. In response to this challenge, the construction industry has turned to advanced technologies that mitigate seismic risk, one of the effective being the Seismic Isolation Bearing.
Seismic Isolation Bearings (SIBs) are gaining traction in modern architecture and engineering due to their ability to isolate a building from the ground motion caused by earthquakes. This technology enables structures to absorb and dissipate the energy released during seismic events, drastically reducing the risk of structural damage and improving overall safety. This article will delve into the role of Seismic Isolation Bearings in earthquake-resistant building designs, exploring their functionality, benefits, and growing adoption worldwide.
What is a Seismic Isolation Bearing?
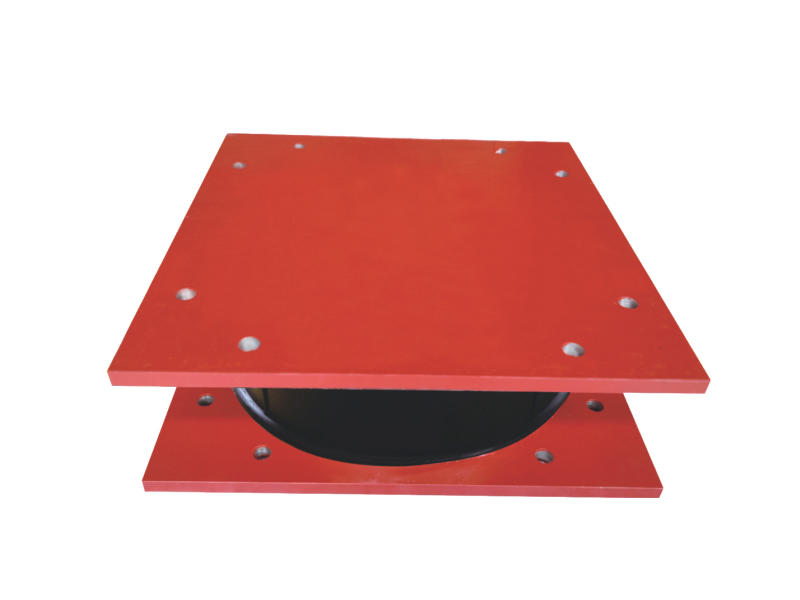
A Seismic Isolation Bearing is a type of base isolator that is placed between a building’s foundation and the superstructure to protect the structure from seismic forces. These bearings typically consist of a combination of elastomeric materials, such as rubber, and other components, such as steel, lead, or other energy-dissipating materials. Their primary function is to decouple the building from the seismic waves generated by an earthquake, allowing the building to move independently of the ground shaking.
When an earthquake occurs, seismic waves travel through the earth, causing the ground to shake. In a traditional structure, these seismic forces are directly transferred into the building, which may result in significant structural damage or even collapse. However, by incorporating Seismic Isolation Bearings into the foundation, the forces of the earthquake are absorbed by the isolators, preventing them from reaching the building's structure and reducing vibrations.
How Do Seismic Isolation Bearings Work?
The operation of Seismic Isolation Bearings is based on two key principles: flexibility and energy dissipation. These bearings are designed to be flexible, allowing the building to move in response to the seismic waves, while also dissipating the energy created by the earthquake’s ground motion. This reduces the amplitude of the shaking felt within the structure and minimizes damage.
When seismic waves hit a building equipped with Seismic Isolation Bearings, the isolation bearings deform, allowing the foundation to shift in response to the ground motion. By decoupling the building from the seismic forces, the bearings allow the structure to remain stable, even in the face of strong shaking.
Additionally, some Seismic Isolation Bearings are equipped with energy-dissipating features, such as lead or viscous dampers, which absorb and dissipate the energy produced during the earthquake. This reduces the intensity of the seismic forces transmitted to the building and further enhances its ability to withstand the shaking.
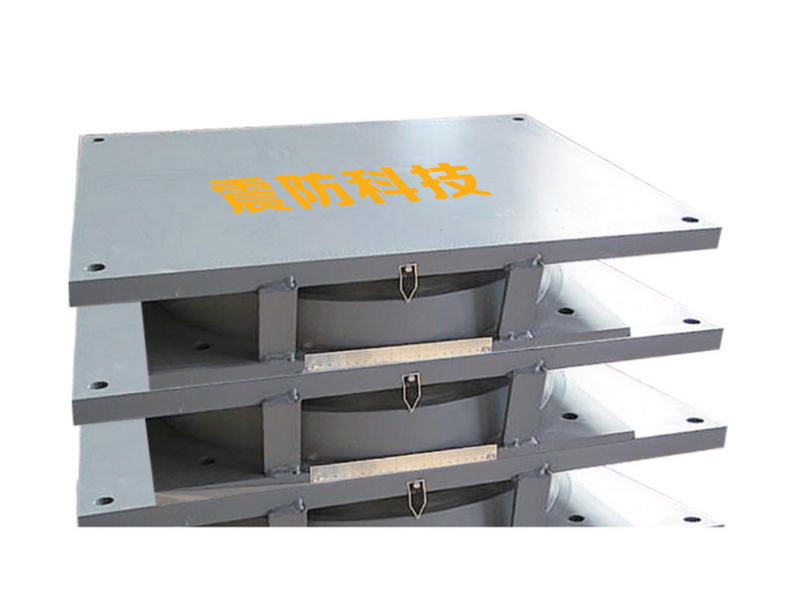

Benefits of Seismic Isolation Bearings
The integration of Seismic Isolation Bearings in earthquake-resistant buildings offers a range of benefits, making them an increasingly popular solution for architects, engineers, and developers in seismic-prone regions.
1. Improved Building Safety
The significant advantage of Seismic Isolation Bearings is the improvement they offer to building safety. By isolating the structure from the ground shaking, these bearings significantly reduce the risk of building collapse or severe damage during an earthquake. This is particularly critical in high-rise buildings, hospitals, schools, and emergency response centers, where the safety of occupants is of paramount importance.
2. Minimizing Structural Damage
Traditional buildings subjected to seismic forces often experience extensive damage, including cracked walls, collapsed floors, and compromised structural elements. Seismic Isolation Bearings, by absorbing and dissipating the seismic energy, prevent these damaging forces from reaching the building’s core structure. This reduces the overall structural damage and minimizes repair costs after an earthquake, ensuring that the building remains functional and safe.
3. Protection of Non-Structural Elements
In addition to safeguarding the core structure of the building, Seismic Isolation Bearings also protect non-structural elements such as windows, doors, partitions, and mechanical systems. These elements are typically more vulnerable to seismic damage, but the decoupling effect provided by the isolation bearings can significantly reduce the likelihood of damage, thereby improving the longevity of the building’s interior systems.