In the realm of seismic engineering and infrastructure resilience, the concept of base isolation using
low damping lead rubber bearings (LRBs) has gained significant traction as a reliable method for mitigating the impact of earthquakes on buildings and structures. Understanding the price dynamics associated with low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation is crucial for stakeholders seeking to balance the costs and benefits of seismic resilience in their projects.
The price of low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation is influenced by various factors, including the size and complexity of the structure, site-specific seismic hazards, regulatory requirements, and the availability of specialized materials and technologies. Engineers and stakeholders must carefully consider these factors when evaluating the overall cost of implementing base isolation with low damping LRBs.
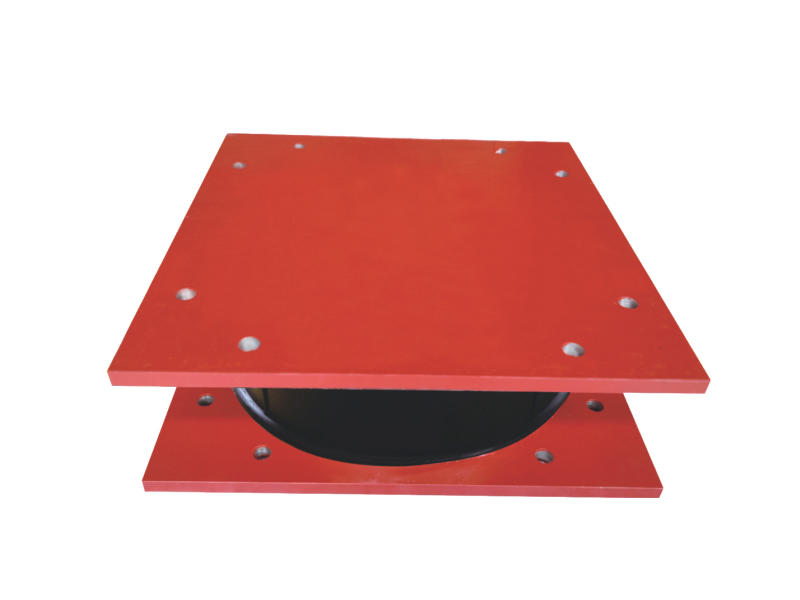
One of the primary cost considerations for low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation is the price of the bearings themselves. Low damping LRBs are constructed using specialized materials, including high-quality rubber compounds and steel components, which contribute to their durability and performance. The cost of procuring these materials, along with the manufacturing processes involved in producing the bearings, impacts their overall price.
Additionally, the installation and construction costs associated with low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation can vary depending on the complexity of the project and site-specific factors. Engineers may need to account for expenses related to site preparation, foundation modifications, and retrofitting existing structures to accommodate base isolation systems. These costs can significantly influence the total price of implementing base isolation with low damping LRBs.
Market demand and supply chain dynamics also play a role in determining the price of low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation. As awareness of seismic risks and the importance of infrastructure resilience grows, the demand for base isolation solutions, including low damping LRBs, continues to increase. Manufacturers may adjust their pricing strategies in response to market dynamics, supply chain disruptions, or changes in demand to remain competitive and profitable.
Furthermore, regulatory requirements and compliance standards impact the price of low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation. Engineers and stakeholders must ensure that base isolation systems meet industry regulations, seismic codes, and certification requirements, which may involve additional testing, documentation, and quality assurance procedures. These regulatory obligations contribute to the overall cost of implementing base isolation with low damping LRBs.
Despite the upfront costs associated with low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation, stakeholders must consider the long-term benefits and cost savings associated with enhanced seismic resilience. Base isolation systems can significantly reduce the risk of structural damage and downtime following an earthquake, resulting in potential savings on repair and restoration expenses. Moreover, the increased safety and reliability of structures can lead to lower insurance premiums and reduced liability risks over time.
Balancing the price of low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation with the benefits of enhanced seismic resilience requires careful consideration of the total cost of ownership and the potential consequences of seismic failure. While upfront costs may seem significant, investing in base isolation with low damping LRBs can yield significant returns in terms of improved safety, reduced structural damage, and long-term cost savings.
Ultimately, the decision to implement low damping lead rubber bearing base isolation should be based on a thorough cost-benefit analysis that considers the unique characteristics and requirements of each project. By understanding the price dynamics and weighing the costs and benefits of base isolation with low damping LRBs, engineers and stakeholders can make informed decisions that prioritize safety, resilience, and economic efficiency in their seismic mitigation strategies.