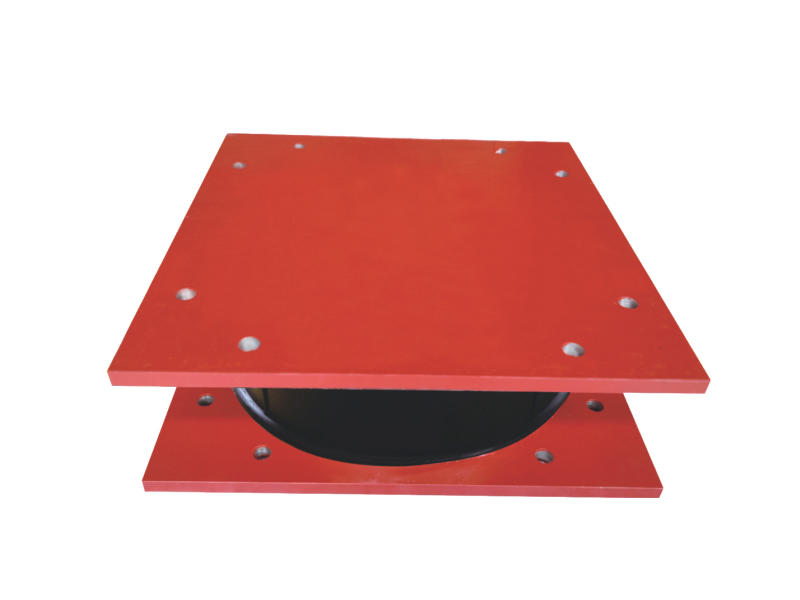
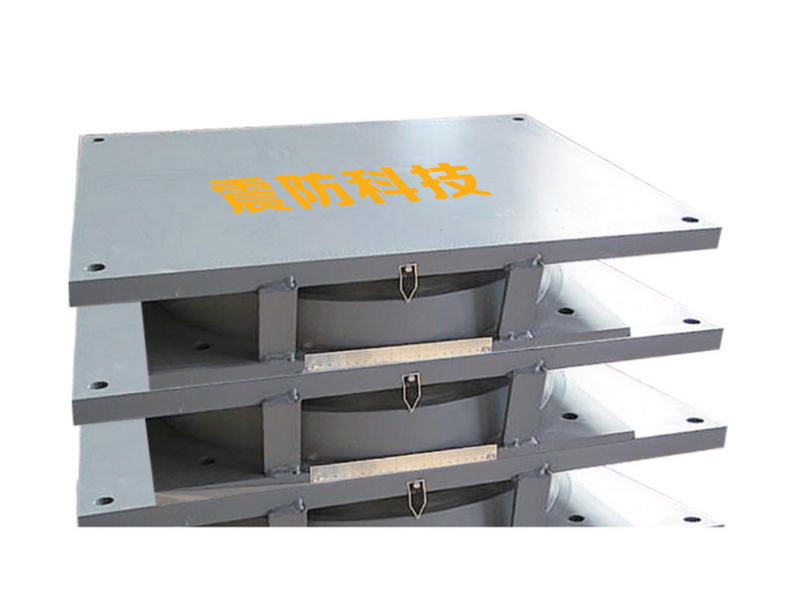
As the world faces ever-increasing seismic challenges, engineers are continuously seeking innovative ways to enhance the resilience of buildings and infrastructure.
Metal Composite Dampers (MHD) have emerged as a cutting-edge technology in seismic engineering, providing an advanced solution to absorb and dissipate earthquake-induced energy. This article explores the concept of Metal Composite Dampers, their mechanism of operation, and the numerous benefits they bring in ensuring the safety and stability of modern structures during seismic events.
Understanding Metal Composite Dampers (MHD)
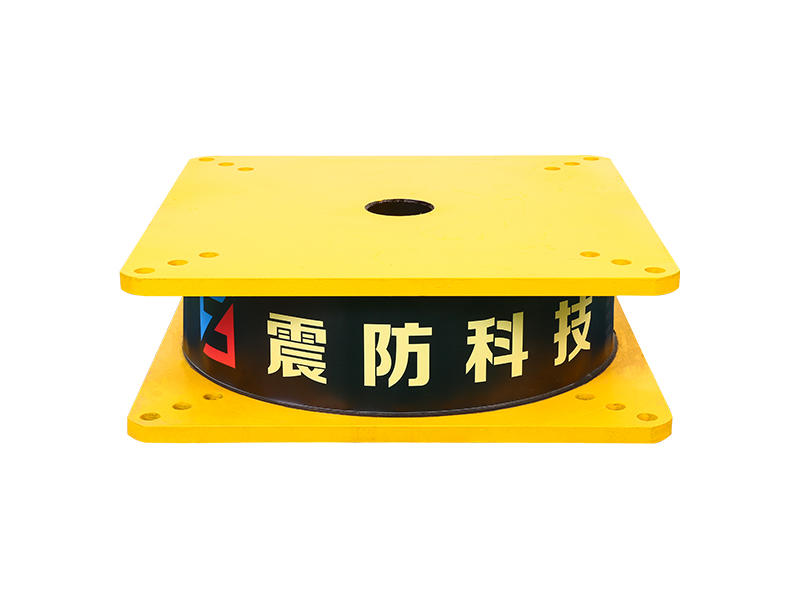
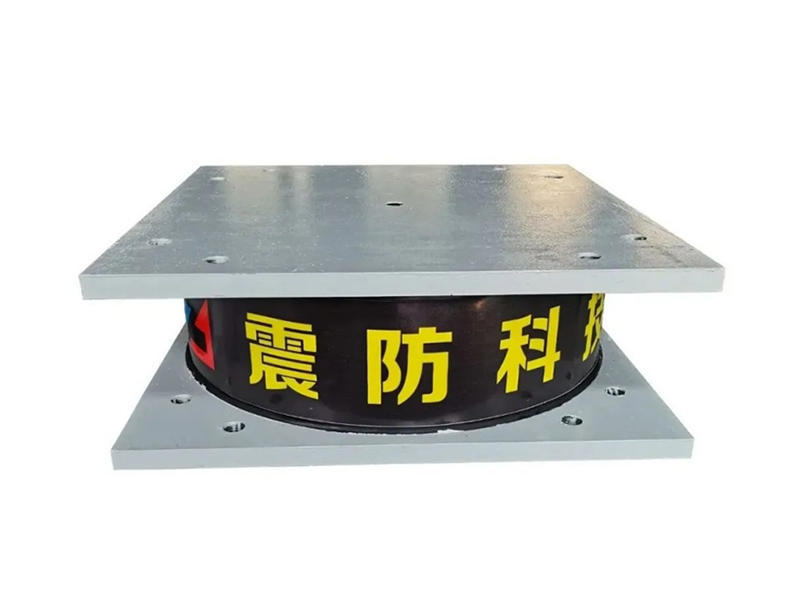
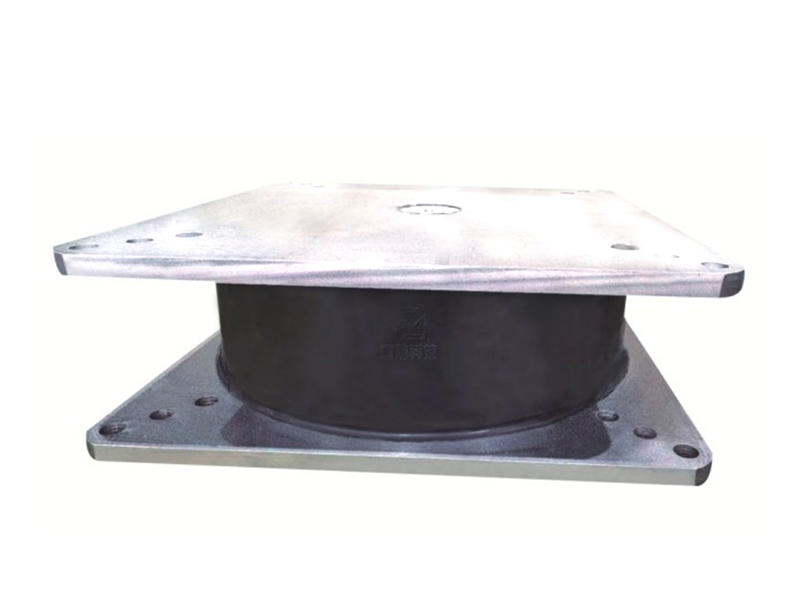
Metal Composite Dampers (MHD) are a class of seismic-resistant devices designed to protect buildings from the damaging effects of earthquakes. They consist of alternating layers of high-strength steel plates and viscoelastic materials, such as rubber or polymers, bonded together to form a composite assembly. This unique arrangement enables MHDs to effectively dampen seismic energy through the combination of metallic strength and viscoelastic energy dissipation.
Functioning of Metal Composite Dampers
During an earthquake, lateral forces cause buildings to sway, subjecting them to significant stress. Metal Composite Dampers are strategically incorporated within the structure to act as energy absorbers. As the building moves laterally, the viscoelastic material within the MHD undergoes deformation, dissipating the kinetic energy of the earthquake into heat. Simultaneously, the high-strength steel plates provide structural integrity, preventing excessive deformations and protecting the building from severe damage.
Advantages of Metal Composite Dampers
a. High Energy Dissipation: The combination of high-strength steel and viscoelastic materials in MHDs results in superior energy dissipation capabilities. This unique synergy enables MHDs to effectively dampen seismic forces, reducing the impact on the building and preserving its structural integrity.
b. Predictable Performance: MHDs offer a predictable and controlled response to seismic forces, allowing engineers to tailor the damper's properties according to the specific needs of the building. This predictability ensures a reliable and consistent performance during earthquakes.
c. Minimal Maintenance: Metal Composite Dampers require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective solution for long-term seismic resilience. Their durability and low maintenance needs contribute to their growing popularity among engineers and building owners.
Integration into Modern Building Designs
Metal Composite Dampers can be seamlessly integrated into modern building designs, offering versatility and adaptability across a wide range of structures. From high-rise buildings to bridges and industrial facilities, MHDs provide an essential addition to safeguarding infrastructure in seismically active regions.
Case Studies and Success Stories
MHDs have demonstrated exceptional performance in various earthquake-prone regions around the world. Case studies from Japan, California, and Taiwan have showcased significant reductions in structural damage and improved building safety, thanks to the successful integration of Metal Composite Dampers.
Advancements in Research and Technology
The ongoing research and advancements in Metal Composite Damper technology are driving further improvements in seismic resilience. Engineers and researchers continue to explore innovative materials, refine manufacturing techniques, and optimize damper configurations to maximize their effectiveness in diverse building applications.
As the world witnesses more frequent and severe seismic events, the significance of innovative seismic engineering solutions becomes increasingly evident. Metal Composite Dampers (MHD) stand at the forefront of this endeavor, offering a powerful tool to enhance building resilience and protect lives during earthquakes. With their exceptional energy dissipation capabilities, predictability, and minimal maintenance needs, MHDs hold the potential to revolutionize seismic engineering and create safer, more resilient urban environments for generations to come. As this technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of seismic-resistant construction worldwide.