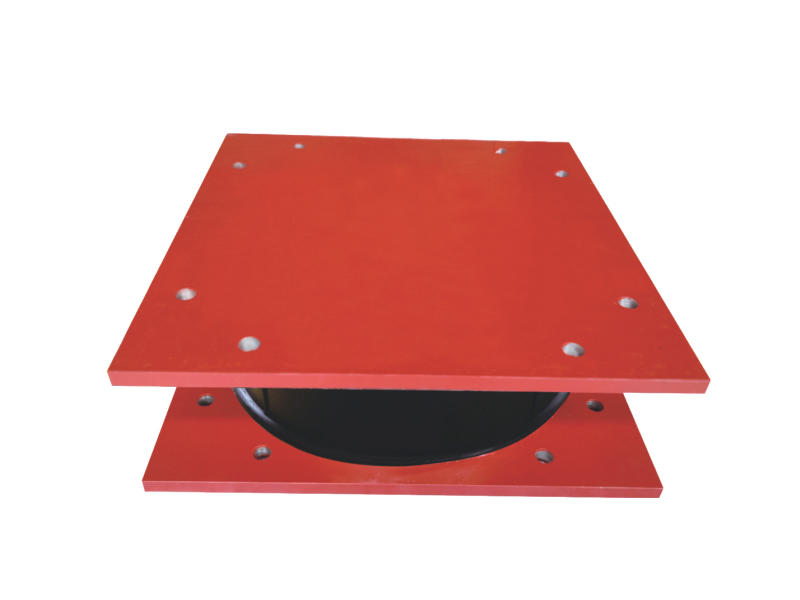
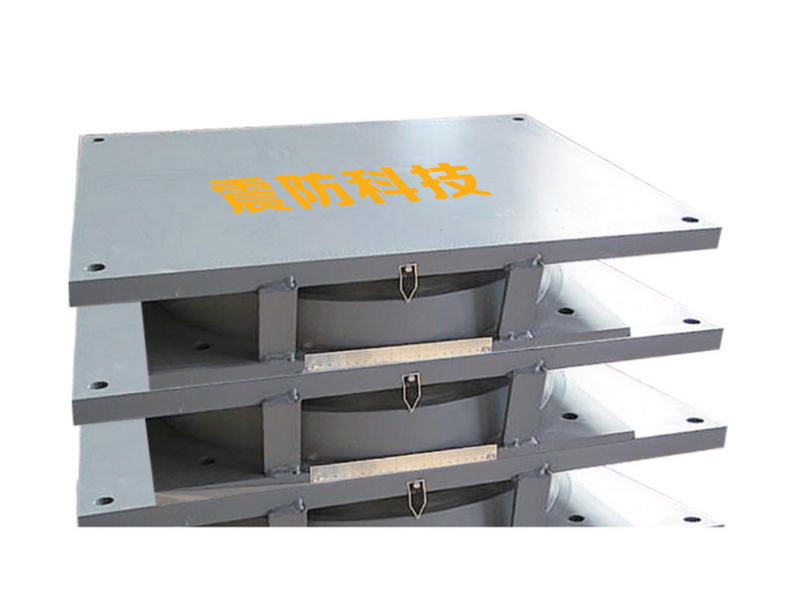
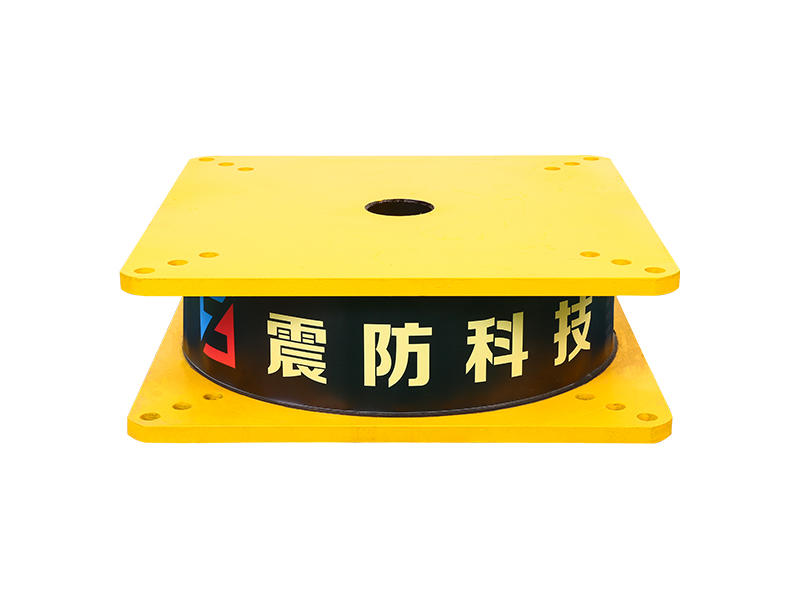
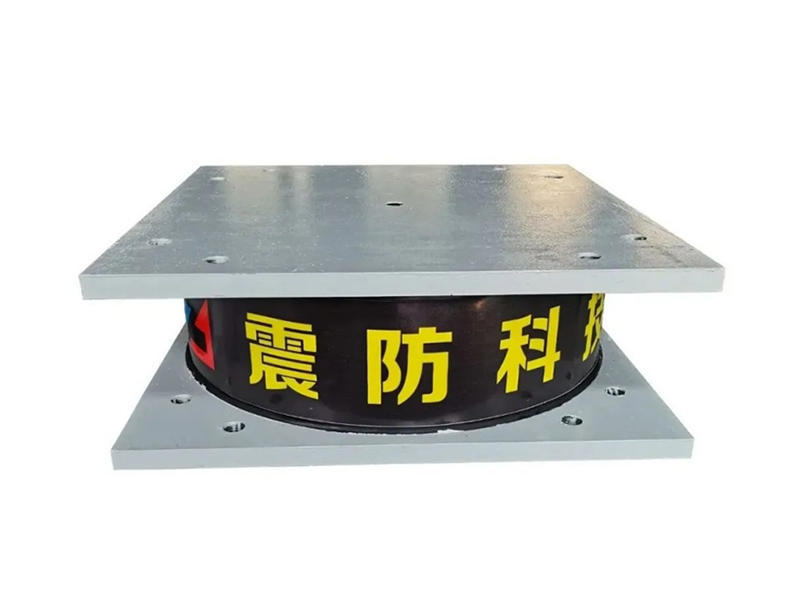
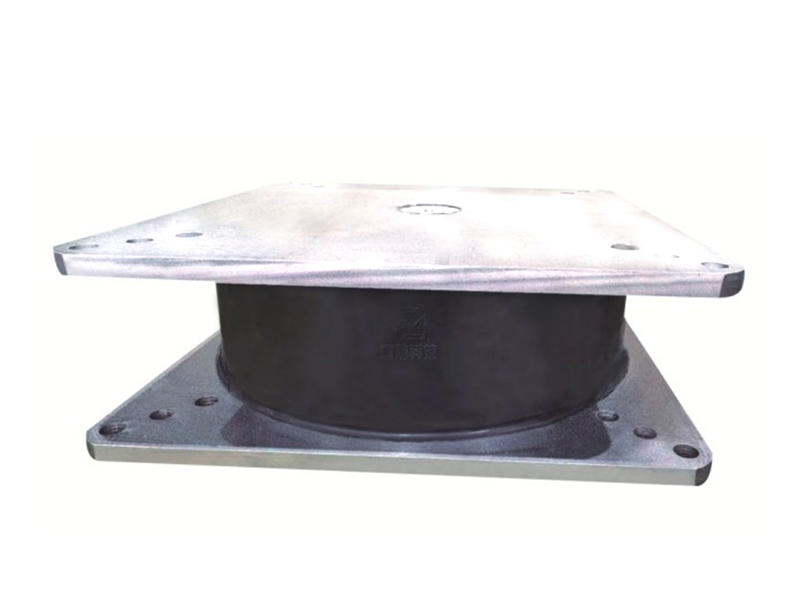
When it comes to machinery and equipment, it’s important to make sure everything is running smoothly and safely. One common tool used to achieve this is a metal damper. But what is a metal damper, and how does it work? In this article, we’ll dive into the world of metal dampers, their functions, and their benefits.
What is a Metal Damper?
A metal damper is a device used to absorb and dissipate energy within a system. Dampers are used in several applications, including HVAC systems, industrial machinery, and even cars. Dampers work by reducing vibration and noise, providing stability, and preventing damage from activities like earthquakes.
A metal damper works by absorbing kinetic energy that is created within a system. The damper takes in this energy, absorbs it, and dissipates it most times in the form of heat. In an HVAC system, for example, a metal damper would take in the kinetic energy created by the air moving through the ducts, then release it as heat.
Dampers are typically made of two metal plates, separated by a thin layer of material. As the kinetic energy moves through the plates, the energy is absorbed by the material that separates them. The thin layer of material could be anything from rubber to a synthetic polymer. The material is chosen based on the specific needs of the machine or system being used.

Benefits of Metal Dampers
There are several benefits to using a metal damper in machinery and equipment:
1. Vibration Reduction: Metal dampers work by reducing vibrations within a machine or system. This, in turn, reduces noise levels and provides stability to the equipment.
2. Safety: Dampers can prevent damage that might occur from sudden movements or environmental challenges like earthquakes. This increases safety for personnel who work with the machines as well as people around the machines.
3. Increased Efficiency: When used in HVAC systems and other equipment, metal dampers can increase efficiency by reducing energy loss that occurs from vibrations and other kinetic energy.
4. Longer Life: Using a metal damper can prolong the life of machinery and equipment by reducing wear and tear. By reducing kinetic energy, the damper prevents materials from breaking down as quickly.
Types of Metal Dampers
There are several different types of metal dampers that can be used in various applications:
1. Spring Dampers: These dampers use a spring to absorb and dissipate energy. Spring dampers are most often used in HVAC systems and other machinery.
2. Friction Dampers: These dampers work by using friction to absorb kinetic energy. They are typically used in high-vibration situations like earthquake-prone areas.
3. Pneumatic Dampers: Pneumatic dampers use air to absorb and dissipate energy. They are often used in automotive engines and other machinery that produces high amounts of kinetic energy.
4. Hydraulic Dampers: Hydraulic dampers use fluid to absorb kinetic energy. They are commonly used in heavy machinery like cranes and excavators.
Metal dampers are an essential part of many machines and systems. These devices work to reduce vibrations, provide stability, and increase safety. Additionally, they increase efficiency and prolong the life of equipment. There are several types of metal dampers available, each suited to specific applications. The next time you use a piece of machinery, take a moment to appreciate the importance of metal dampers and how they work to make our lives safer and more efficient.