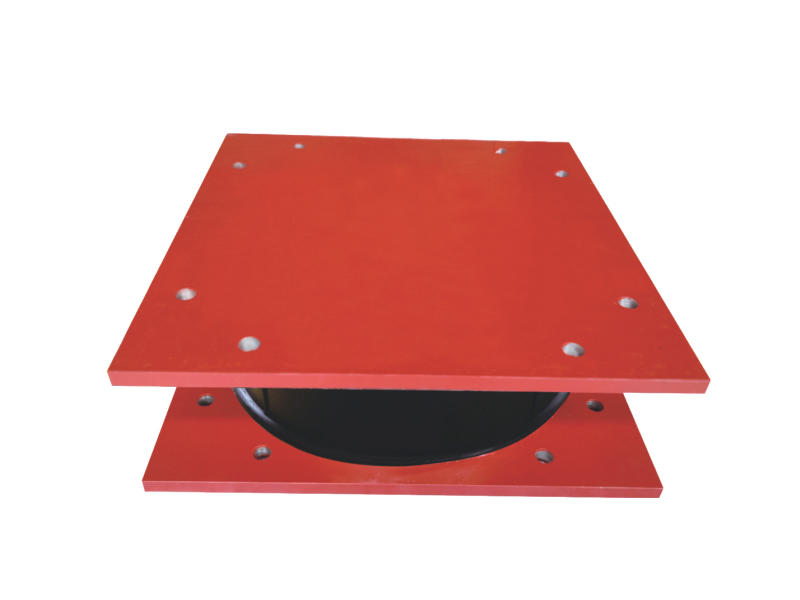
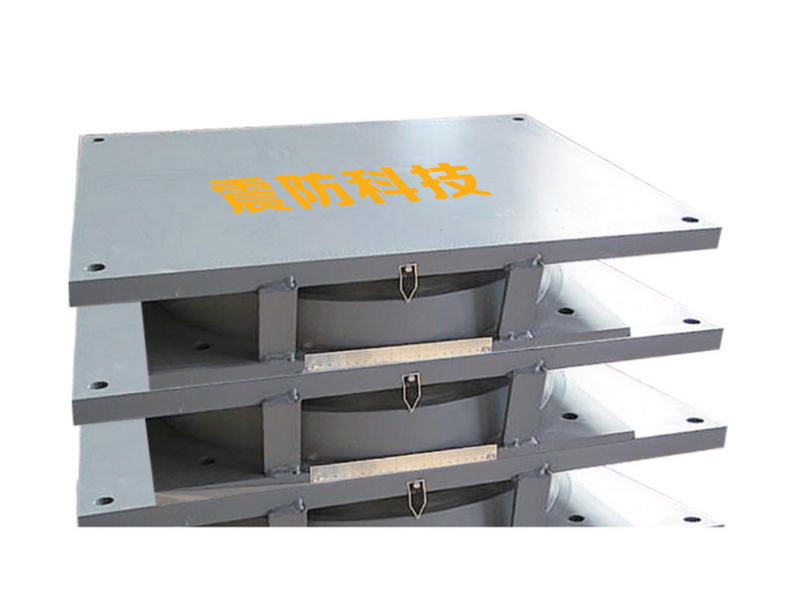
In many mechanical systems, shock absorption is a critical requirement for safe and reliable operation. Vibrations and shocks can cause damage to equipment, reduce productivity, and even lead to catastrophic failures. To address this problem, engineers have developed various types of dampers that can absorb and dissipate shock energy. Among these, metal dampers have proven to be a reliable and effective solution.
Metal dampers are mechanical devices that are designed to absorb and dissipate shock energy by converting it into heat or other forms of energy. They consist of a metal structure that is attached to the equipment or structure that needs to be protected. When subjected to a shock or vibration, the metal structure undergoes deformation, which absorbs the energy and reduces the amplitude and duration of the shock.

There are several types of
metal dampers available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some common types include:
Coil Spring Dampers: These dampers use a coil spring to absorb shock energy. They are simple and reliable, but they can be bulky and have limited damping capacity.
Friction Dampers: These dampers use the friction between two metal surfaces to absorb shock energy. They are compact and have a high damping capacity, but they can wear out quickly and require regular maintenance.
Viscoelastic Dampers: These dampers use a viscoelastic material, such as rubber or silicone, to absorb shock energy. They are lightweight and have a high damping capacity, but they can be expensive and have a limited temperature range.
Fluid Dampers: These dampers use a fluid, such as oil or water, to absorb shock energy. They are versatile and have a high damping capacity, but they can be messy and require regular maintenance.
Metal dampers can be used in a variety of applications, including:
Industrial Machinery: Metal dampers are commonly used in heavy machinery to reduce vibrations and shocks that can damage the equipment and reduce productivity.
Bridges: Metal dampers are often used in bridge structures to reduce the effects of wind, earthquakes, and other external forces.
Automotive: Metal dampers are used in automotive suspension systems to provide a smooth and stable ride.
Aerospace: Metal dampers are used in aerospace applications to reduce vibrations and shocks that can affect the performance and safety of the aircraft.